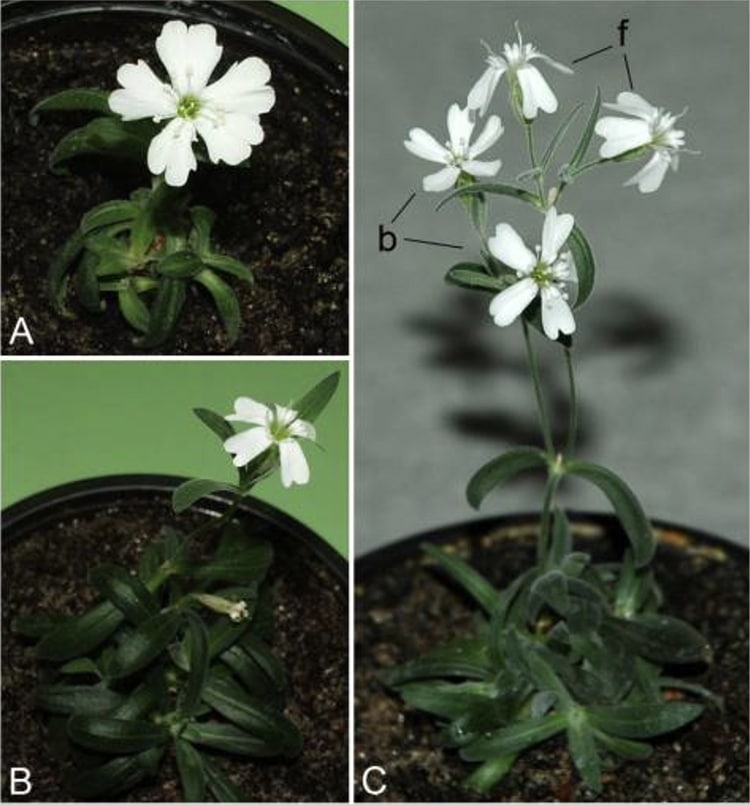
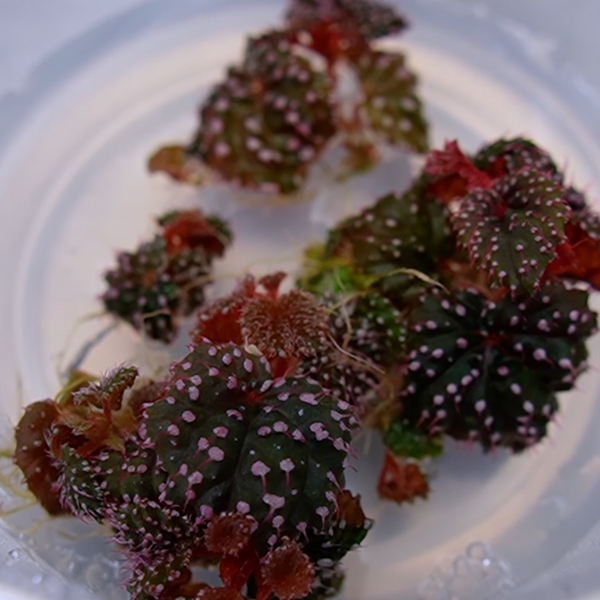
Flowering plants of Silene stenophylla. (Photo: S. Yashina et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012, Figure 3)
Many prehistoric secrets lie in the permafrost of the world's arctic regions. Whether its a well-preserved mammoth or ancient plants, scientists can learn a lot from these biological discoveries. In 2012, a Russian team regenerated a series of fertile, flowering Silene stenophylla plants from 32,000-year-old seed pods. This impressive accomplishment was detailed in a paper in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences—an accomplishment which foreshadows other developments that could emerge from the permafrost.
The discovery of the prehistoric seed pods was part of the larger excavation of ancient ground squirrel hibernation burrows in ice deposits in Siberia. The squirrels' food supplies had been trapped and preserved in the burrows, providing a wealth of biological evidence. The fruit of the Silene stenophylla specifically date to about 32,000 years ago in the Pleistocene epoch. They presented a challenge for the researchers at the Russian Academy of Scientists. Previously, the oldest regenerated plant was a Judean date palm dating to about 2,000 years ago.
The Russian team first tried to use mature seeds from the fruit pods. However, these seeds could not generate a plant. The team then tried placental tissue from immature seeds. Using cloning technology, 36 plants were bred from the ancient material. While they looked like the modern Silene stenophylla which still grows in the area, once the plants flowered, the petals were spaced further apart than in the modern version. Interestingly, the ancient plants produced seeds which generated new plants 100% of the time—a better rate than the modern variety.
These 32,000-year-old plants might be the key to unlocking further secrets of the permafrost.
Scientists in Russia resurrected a 32,000-year-old plant from the Siberian permafrost.
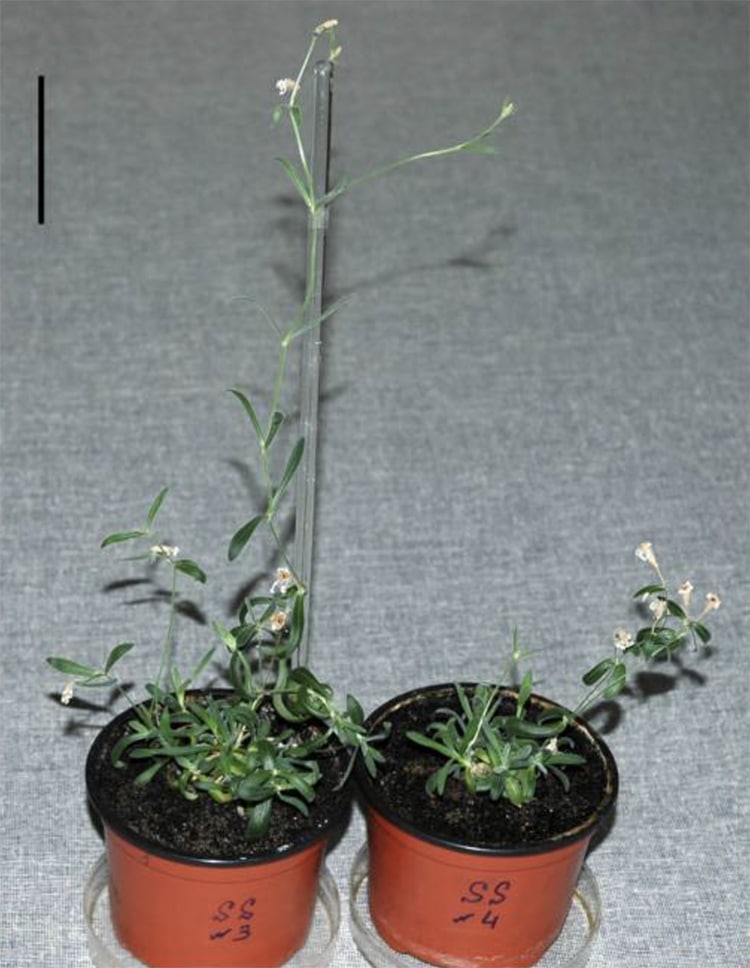

The Silene stenophylla plant fruiting. (Photo: S. Yashina et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012, Figure 2)
Using cloning technology and the placental tissue of immature seeds, the team raised 36 plants.
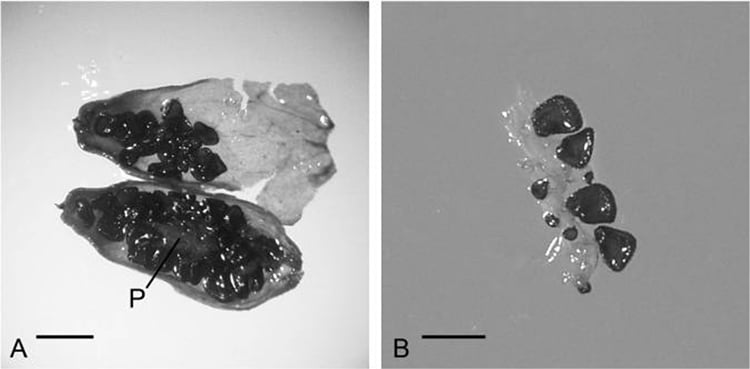
The immature fruit of Silene stenophylla which was discovered in the permafrost. (Photo: S. Yashina et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012, Figure 4)
The ancient plants were similar to the modern variety, with slightly larger and widely-spaced petals.
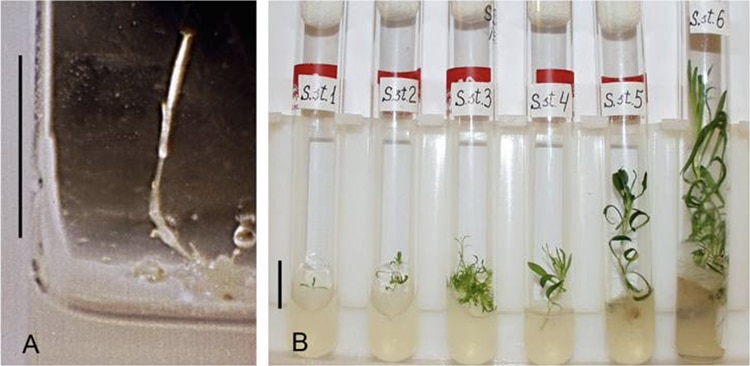
Cloning the Silene stenophylla from the discovered fruit placenta cells. (Photo: S. Yashina et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012, Figure 5)
h/t: [Earthly Mission]
Related Articles:
Climate Change Brings Prehistoric Plant From 60 Million Years Ago Back to Life
15,000-Year-Old Bison Sculptures Are Perfectly Preserved in a French Cave
World’s Oldest DNA Is Discovered in a 1.2-Million-Year-Old Mammoth
Discovery of a 9,000 Year-Old Burial of a Female Hunter Challenges Prehistoric Gender Roles
Colorful 225-Million-Year-Old Fossils Are Just One Highlight of This Stunning National Park